Understanding Sleep Apnea: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options

Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that can have serious health consequences if left untreated. It occurs when a person's breathing is interrupted during sleep, leading to a lack of oxygen and potentially dangerous complications. In this guide, we'll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for sleep apnea.
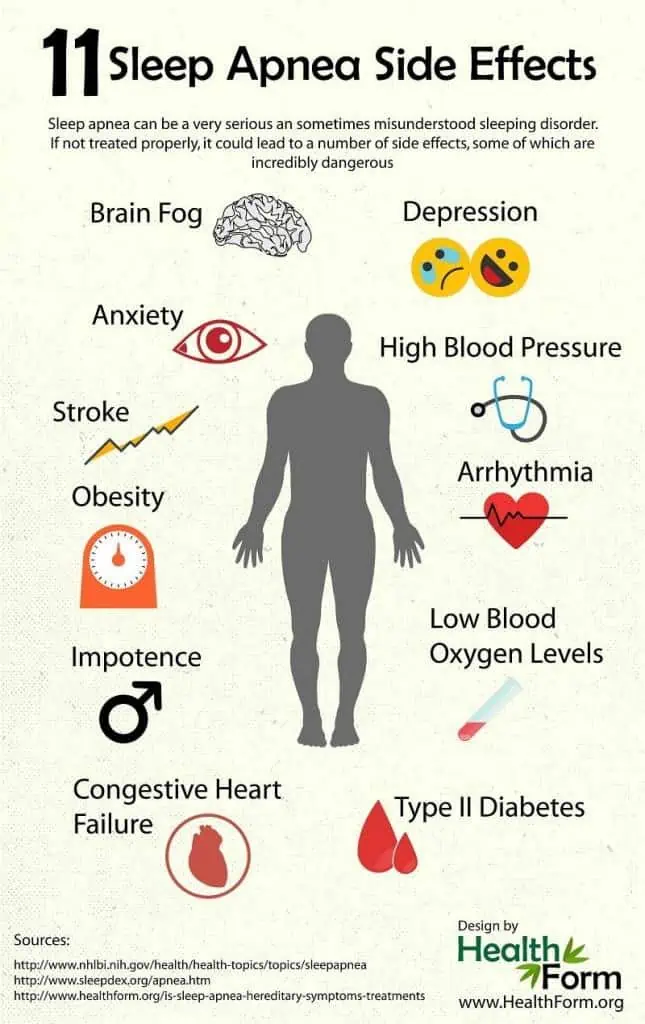
Sleep apnea is a serious medical condition that can lead to complications if left untreated. The most common symptoms of obstructive and central sleep apnea include loud snoring, gasping for air during sleep, awakening with a dry mouth, morning headache, difficulty staying asleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty paying attention while awake, and irritability. However, not everyone who has sleep apnea snores, so it is important to talk to a healthcare provider if you have symptoms of sleep apnea.
What is sleep apnea?
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep. These pauses can last anywhere from a few seconds to a few minutes and can occur multiple times throughout the night. As a result, the person with sleep apnea may experience disrupted sleep and a lack of oxygen, which can lead to a range of health problems. There are two main types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea, which is caused by a blockage in the airway, and central sleep apnea, which is caused by a failure of the brain to signal the muscles to breathe.
Obstructive sleep apnea is the more common type, and it often goes undiagnosed. Symptoms of sleep apnea include loud snoring, gasping or choking during sleep, daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, and difficulty concentrating. Risk factors for sleep apnea include obesity, smoking, alcohol use, and a family history of the disorder. Treatment options for sleep apnea include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and quitting smoking, as well as the use of a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine or other devices to help keep the airway open during sleep. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have sleep apnea, as untreated sleep apnea can lead to serious health problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
Types of Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by abnormal breathing patterns during sleep. There are three types of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea (CSA), and complex sleep apnea syndrome (CompSA). OSA is the most common type of sleep apnea, occurring when the muscles in the back of the throat relax too much to allow normal breathing. This results in a blockage of the airway, causing a person to stop breathing during sleep. A noticeable sign of OSA is snoring. CSA occurs when the brain fails to send the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. Unlike OSA, there is no snoring with CSA. CompSA is a combination of OSA and CSA.
The symptoms of sleep apnea include loud snoring, episodes in which a person stops breathing during sleep, gasping for air during sleep, awakening with a dry mouth, morning headache, difficulty staying asleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, difficulty paying attention while awake, and irritability. If a person experiences any of these symptoms, they should see a healthcare provider.
Treatment for sleep apnea can ease symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment options include continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), bilevel positive airway pressure (BPAP), and adaptive servo-ventilation (ASV). CPAP is a machine that continuously blows air into the throat via a mask worn over the nose or nose and mouth, keeping the airway open. BPAP delivers a preset amount of air pressure to the airway, providing more pressure when a person inhales and less pressure when they exhale. ASV is a machine that monitors a person's breathing patterns and adjusts the air pressure accordingly.
The most common type of sleep apnea is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which occurs when the throat muscles intermittently relax and block the airway during sleep, leading to loud snoring, gasping for air, and pauses in breathing. OSA is caused by relaxation of soft tissue in the back of the throat that blocks the passage of air. Central sleep apnea (CSA) is less common and is caused by irregularities in the brain's signals to breathe. Complex sleep apnea syndrome (CompSA) is a combination of OSA and CSA. Knowing about the different types of sleep apnea can help a person identify the cause of their symptoms and seek the right medical care.
Causes of sleep apnea
The causes of sleep apnea can vary depending on the type of sleep apnea a person has. Obstructive sleep apnea is typically caused by a blockage in the airway, which can be due to factors such as obesity, enlarged tonsils or adenoids, or a narrow airway. Central sleep apnea, on the other hand, is caused by a failure of the brain to signal the muscles to breathe. This can be due to underlying medical conditions such as heart failure, stroke, or Parkinson’s disease. Other risk factors for sleep apnea include being male, over the age of 40, having a family history of sleep apnea, and smoking.
Obstructive sleep apnea is the most common type of sleep apnea, and it occurs when the muscles in the back of the throat fail to keep the airway open during sleep. This can be due to excess weight, which can cause fat deposits to accumulate in the throat and narrow the airway. Enlarged tonsils or adenoids can also block the airway, as can a naturally narrow airway. Central sleep apnea, on the other hand, is caused by a failure of the brain to signal the muscles to breathe. This can be due to underlying medical conditions such as heart failure, stroke, or Parkinson’s disease. Other risk factors for sleep apnea include being male, over the age of 40, having a family history of sleep apnea, and smoking. It’s important to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have sleep apnea, as it can lead to serious health complications if left untreated.
Symptoms of sleep apnea
The most common symptom of sleep apnea is loud snoring, often accompanied by gasping or choking sounds. Other symptoms can include excessive daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and mood changes. It’s important to note that not everyone with sleep apnea will experience all of these symptoms, and some people may not even realize they have the condition. If you suspect you may have sleep apnea, it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In addition to loud snoring and gasping or choking sounds, sleep apnea can also cause pauses in breathing during sleep, which can lead to waking up abruptly and feeling short of breath. This can happen multiple times throughout the night, leading to poor quality sleep and daytime fatigue. Other symptoms can include dry mouth or sore throat upon waking, restless sleep, and even depression or anxiety. It’s important to take these symptoms seriously and seek medical attention if you suspect you may have sleep apnea. Treatment options can include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bed, as well as the use of a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine during sleep.
Diagnosis and treatment options
If you suspect you have sleep apnea, it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Diagnosis typically involves a sleep study, which can be done in a sleep lab or at home with a portable monitor. Treatment options may include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss or avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bed, as well as the use of a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine or other devices to help keep the airway open during sleep. In some cases, surgery may be recommended. It’s important to work with your healthcare provider to find the best treatment plan for your individual needs.
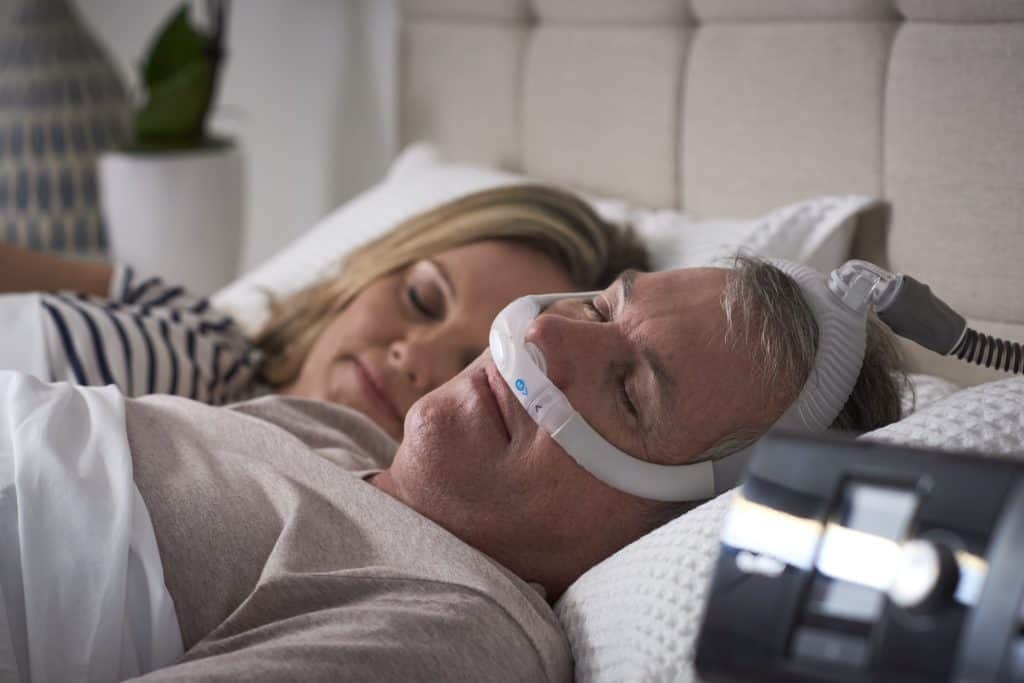

Once diagnosed with sleep apnea, there are several treatment options available. Lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bed, and sleeping on your side instead of your back, can all help reduce symptoms. In addition, using a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine can be highly effective in keeping the airway open during sleep. Other devices, such as oral appliances or positional therapy devices, may also be recommended. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct structural issues in the airway. It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs and to ensure that your sleep apnea is properly managed.
Lifestyle changes to manage sleep apnea
Lifestyle changes can be an effective way to manage sleep apnea, especially for those with mild to moderate cases. Losing weight, avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bed, and sleeping on your side instead of your back can all help reduce the severity of sleep apnea symptoms. Additionally, quitting smoking and practicing good sleep hygiene, such as sticking to a regular sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine, can also improve sleep quality and reduce the risk of sleep apnea. It’s important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the best lifestyle changes for your individual needs.
One of the most effective lifestyle changes for managing sleep apnea is weight loss. Excess weight can put pressure on the airway, making it more difficult to breathe during sleep. Losing even a small amount of weight can improve symptoms and reduce the severity of sleep apnea. Avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bed is also important, as these substances can relax the muscles in the throat and make it more difficult to breathe. Sleeping on your side instead of your back can also help keep the airway open and reduce snoring. Quitting smoking is another important lifestyle change, as smoking can irritate the airway and increase inflammation. Finally, practicing good sleep hygiene, such as sticking to a regular sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine, can help improve sleep quality and reduce the risk of sleep apnea. It’s important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the best lifestyle changes for your individual needs.
According to the provided sources, sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people in the United States. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common type of sleep apnea, and it is caused by relaxation of soft tissue in the back of the throat that blocks the passage of air. It is estimated that approximately 6.62% of the total American population, or 18 million Americans, have sleep apnea. However, it is important to note that many cases of sleep apnea go undiagnosed, so the actual number of people affected may be higher. If you suspect you may have sleep apnea, it is important to see a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people in the United States. There are three main forms of sleep apnea: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea (CSA), and complex sleep apnea syndrome (CompSA). OSA is the most common type of sleep apnea and is caused by relaxation of soft tissue in the back of the throat that blocks the passage of air. CSA is caused by irregularities in the brain's signals to breathe. Sleep apnea can cause excessive daytime sleepiness, loud snoring, morning headache, dry mouth upon awakening, and restless sleep with periods of wakefulness. If left untreated, sleep apnea can be life-threatening and increase the risk of stroke and other complications. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and avoiding alcohol and sedatives, and medical interventions, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy and surgery.